Krunal Shah
Dec 31, 2025
Key Highlights
A mutual NDA, or bilateral NDA, is a two-way confidentiality agreement where both parties protect each other's secrets.
It establishes reciprocal obligations, meaning each party is both a discloser and a recipient of confidential information.
This type of agreement is crucial for joint ventures, mergers, and collaborative partnerships.
A mutual NDA fosters trust, encouraging open discussion during a business relationship.
It provides balanced legal protection, setting a fair foundation for negotiations.
When two businesses explore a potential partnership, they often need to share sensitive data. How do you ensure your company's secrets remain safe? A mutual NDA is a vital legal tool that protects the confidential information of all parties involved. This agreement creates a secure framework for open discussions, allowing your business relationship to develop on a foundation of trust and mutual respect from the very beginning.
Understanding Mutual NDAs

A mutual NDA is a type of confidentiality agreement designed for situations where information flows in both directions. Unlike agreements that protect only one party, this document ensures that any sensitive information or business information shared between two parties is kept private by both.
Understanding the mechanics of a mutual NDA helps you choose the right legal protection. Let's examine what a mutual NDA is, how its "two-way" nature works, and how it compares to a unilateral NDA.
What is a Mutual NDA?
A mutual non-disclosure agreement, also known as a bilateral NDA, is a legally binding contract where two or more parties agree to protect the confidential information they share. The core principle is reciprocity, where everyone involved has the same duties.
In this arrangement, each party acts as both a disclosing party and a receiving party. This means you are simultaneously sharing your private data while also being trusted with the other party's secrets.
This two-way protection creates a level playing field, making it an ideal choice for collaborative business ventures where open communication is key to success.
The Concept of "Two-Way" Confidentiality
The defining feature of a mutual NDA is its "two-way" confidentiality. This means the contract imposes reciprocal obligations on everyone who signs it. Both parties are equally bound by the same rules to protect the other party’s confidential information.
These shared confidentiality obligations ensure fairness. You are not the only one promising to keep secrets; the other party is making the exact same promise to you.
This structure builds trust and security from the start. Knowing your sensitive data is protected encourages more transparent and productive discussions, as both sides can share confidential information with confidence.
Mutual NDA vs Unilateral NDA
Choosing between different types of NDAs depends entirely on how information will be shared. A unilateral NDA is for one-way disclosures, while a mutual NDA is for two-way exchanges.
In a unilateral NDA, only one disclosing party shares sensitive information, and only the receiving party is obligated to protect it. This is common when a startup pitches to an investor.
A mutual NDA is necessary when both parties are sharing and receiving confidential data. The table below highlights the key differences.
Aspect | Unilateral NDA | Mutual NDA |
|---|---|---|
Who Discloses? | One party (Discloser) | Both parties |
Who is Obligated? | One party (Recipient) | Both parties |
Information Flow | One-way | Two-way |
Common Use Cases | Employee onboarding, pitches | Partnerships, M&A, joint ventures |
Related Article: Types of Contracts Every Business Needs
Key Situations Where Mutual NDAs Are Used

A mutual NDA is the best choice whenever a business relationship involves a two-way exchange of confidential information. Using one sets clear expectations and protects both sides during a potential business partnership. If both parties are bringing valuable, private data to the table, a mutual NDA ensures fairness.
These agreements are vital for building trust in several key scenarios, including joint ventures, M&A negotiations, and other collaborative projects where sensitive information must be shared.
Joint Ventures and Strategic Partnerships
When two companies consider forming joint ventures or strategic alliances, they need to exchange proprietary information to evaluate the opportunity. A mutual NDA is essential in these situations to protect both parties' interests.
During these discussions, you may need to share sensitive business information. A mutual agreement ensures this data remains confidential, preventing one side from gaining an unfair competitive advantage.
Commonly shared information includes:
Technology and intellectual property
Business plans and financial projections
Customer data and market strategies
Mergers and Acquisition (M&A) Negotiations
During mergers and acquisitions (M&A), both the acquiring company and the target company must disclose highly sensitive information. The due diligence phase requires a thorough review of each other's operations, finances, and strategies.
A mutual NDA is critical to protect this confidential information throughout the complex negotiation process. It creates a secure environment for both parties to conduct a detailed evaluation without fear of data leaks.
Information shared during M&A often includes:
Detailed financial data and records
Operational procedures and trade secrets
Strategic plans and customer information
Business Collaborations and Partnerships
Any business relationship that involves co-developing a product, service, or technology requires a mutual NDA. If both parties are contributing intellectual property or other proprietary data, a two-way agreement is necessary.
This is common in technology collaborations, research projects, and even partnerships with service providers where you might learn about their proprietary methods. A mutual NDA ensures both sides can collaborate freely.
Examples of information exchanged include:
Software source code or APIs
Unreleased product features
Proprietary algorithms or user data insights
Essential Elements in a Mutual Non-Disclosure Agreement
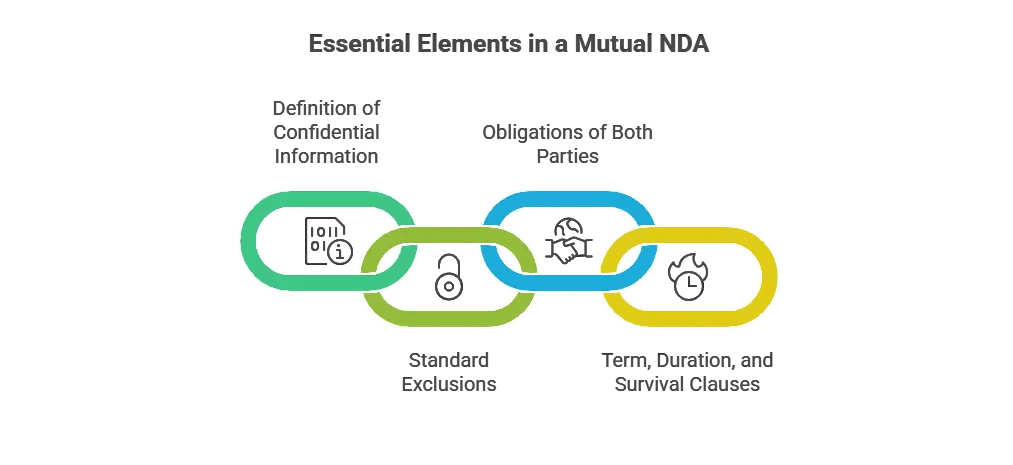
A strong mutual NDA is more than a simple promise; it's a detailed legal contract outlining specific rights and confidentiality obligations. While many NDA templates exist, a well-drafted agreement defines exactly what is protected and what the receiving party must do with the proprietary information.
To ensure your confidential information is secure, it is vital to understand the key clauses that make up an effective agreement. Here are the essential components every mutual NDA should include.
Definition of Confidential Information
This is one of the most important clauses in the agreement. It must clearly specify what types of disclosed information are considered confidential. The definition should be broad enough to cover all sensitive data but precise enough to be legally enforceable.
Examples of business information often covered include trade secrets, financial data, customer lists, and marketing strategies. Clearly labelling documents as "Confidential" is also a good practice.
A vague definition can leave your proprietary information vulnerable. Ensure this clause accurately reflects the sensitive data you intend to protect throughout your business discussions.
Standard Exclusions from Confidentiality
Not all shared information can be kept secret. The exclusions clause carves out specific exceptions to the confidentiality rules. This section is crucial for preventing future disputes over what was and wasn't protected.
Common exclusions include public information that is already widely known or becomes public without fault of the receiving party. Information that was rightfully in one party's possession before the agreement is also typically excluded.
Other standard exclusions cover information lawfully received from third parties without confidentiality restrictions or data that is independently developed without reference to the shared secrets.
Obligations of Both Parties under a Mutual NDA
This section details the core obligations of each party under the confidentiality clause. Since it's a mutual agreement, these duties apply equally to both the disclosing party and the receiving party when they handle the other's business information.
These rules set clear boundaries on how confidential data can be used and protected. Each party must treat the other's information with a reasonable standard of care, similar to how they protect their own secrets.
Key obligations typically include:
Non-disclosure: Not sharing information with unauthorised third parties.
Non-use: Using the information only for the agreed-upon purpose.
Protection: Taking reasonable steps to secure the information from leaks.
Term, Duration, and Survival Clauses
It's important to distinguish between the agreement's term and the duration of confidentiality. The term defines how long the legal contract is active for sharing information, often starting from its effective date.
The duration of confidentiality, however, specifies how long the protection obligation lasts, which can extend years beyond the end of the business relationship. For highly sensitive trade secrets, this obligation may last indefinitely.
Survival clauses ensure that confidentiality duties remain in effect even after the main agreement terminates. This is crucial for long-term protection of your valuable information.
Related Article: Contract Management Security: Risks, Mistakes and Solutions
Structure and Customisation of Mutual NDAs

While the basic structure of a mutual NDA is consistent, it is not a one-size-fits-all legal contract. Different industries may have unique risks, requiring tailored clauses. Using standard NDA templates is a good starting point, but customisation is key to ensuring adequate protection.
Following best practices means adapting the agreement to your specific needs. Let's look at the typical layout of these types of NDAs and how you can customise them effectively.
Typical Layout of a Mutual NDA Template
Most mutual NDA templates follow a standard format designed to cover the essential aspects of a confidential business relationship. Understanding this layout helps you review any proposed legal contract and identify if key protections are missing.
This typical structure ensures that the agreement clearly defines the parties, the information being protected, and the rules governing its use. While you can find many free contract templates online, always review them carefully.
A standard template for this type of NDA usually includes:
Identification of the parties involved.
A detailed definition of what constitutes confidential information.
The confidentiality clause, outlining the obligations of each party.
Customising Clauses for Your Business Needs
Relying solely on a generic template can be risky. NDA customisation is crucial, especially when high-value intellectual property or unique business strategies are involved. You should tailor clauses to fit the specific context of your discussions.
For complex transactions like mergers or joint ventures, seeking legal counsel is highly recommended. A lawyer can help draft language that protects your interests and aligns with your long-term goals.
Areas that often require customisation include:
The specific definition of confidential data.
The duration of the confidentiality obligations.
Clauses related to the return or destruction of information.
Main Benefits of Using a Mutual NDA
Using a mutual NDA offers significant advantages when navigating a business relationship that requires sharing proprietary information. The primary benefit is that both parties receive equal legal protection, which fosters a sense of fairness and security for the confidential information being shared.
This balanced approach builds trust and encourages open dialogue, which is essential for evaluating potential collaborations. Let’s explore the main benefits of this agreement in more detail.
Balanced and Reciprocal Legal Protection
The most significant benefit of a mutual NDA is the balanced legal protection it provides. Because the contract imposes reciprocal obligations, both parties' proprietary data and confidential information are equally safeguarded.
This creates a level playing field, which can set a positive and fair tone for the entire business relationship. Neither party is at a disadvantage, as the rules apply to everyone in the same way.
The key advantages of this balanced approach are:
Fairness: It is seen as more equitable than a one-sided agreement.
Security: Both parties know their sensitive information is protected.
Trust: It shows a mutual commitment to protecting each other's interests.
Encouraging Open Collaboration
When both parties in a business relationship feel secure, they are more likely to engage in open and honest collaboration. A mutual NDA provides the legal safeguards needed to remove hesitation about sharing sensitive information.
This security encourages deeper discussions, allowing for a more thorough evaluation of potential partnerships and business strategies. You can share confidential information with the confidence that it will be used only for the stated purpose. By reducing the fear of data misuse, a mutual NDA paves the way for more productive and transparent negotiations.
Limiting Risks During Sensitive Discussions
Sensitive discussions about business plans or technology carry inherent risks. A mutual NDA is a powerful tool for limiting these risks by establishing clear legal consequences for any breach of confidentiality.
If a party violates the agreement, the harmed party has a clear path for legal recourse. The contract often specifies that monetary damages may not be enough, allowing the disclosing party to seek injunctive relief to stop the breach.
Key risk-limiting features include:
Legal Framework: Provides a basis for taking legal action.
Deterrence: The threat of legal consequences discourages misuse of information.
Remedies: Defines options like injunctive relief to prevent further harm.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Drafting a Mutual NDA

Drafting a mutual NDA requires careful attention to detail, as simple mistakes can weaken its protections or even render it unenforceable. One common error is using overly broad language, which can create ambiguity and future disputes. It is also crucial to manage these agreements effectively after they are signed. Good NDA management involves tracking key dates and obligations to ensure compliance.
For instance, using advanced CLM software can automate reminders and centralise your contracts. Adhering to best practices and seeking legal advice can help you avoid pitfalls that could expose your confidential data and business information.
Overly Broad or Vague Definitions
One of the most critical mistakes is using vague definitions for confidential information. If the scope of what is protected is unclear, a court may find the clause difficult to enforce, leaving your proprietary information at risk.
Your agreement should precisely describe the types of disclosed information covered. Ambiguous phrases like "all business information" are often too broad. Instead, specify categories like financial projections, customer lists, or technical data.
To avoid this mistake:
Be specific about what is considered confidential.
Avoid catch-all clauses that are overly broad.
Consult with legal counsel to ensure your definitions are clear and enforceable.
Conclusion
In summary, Mutual NDAs serve as an essential tool for businesses aiming to protect confidential information while fostering collaboration. By understanding the nuances of these "two-way" agreements, companies can effectively navigate partnerships, joint ventures, and sensitive negotiations without fear of compromising proprietary information. The key lies in crafting a well-structured Mutual NDA that encompasses vital elements such as the definition of confidentiality, obligations of both parties, and duration. By avoiding common pitfalls and ensuring clarity, businesses can enjoy balanced legal protection and create an environment conducive to open dialogue. If you're considering drafting a Mutual NDA, reach out today to get a free consultation and ensure your interests are safeguarded.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are mutual NDAs legally binding?
Yes, a mutual NDA is a legally binding legal contract, provided it is drafted correctly. To be enforceable, the confidentiality agreement must have clear terms and be governed by a specific jurisdiction's law. Seeking legal advice can ensure your agreement is valid.
What happens if one party breaches a mutual NDA?
If a breach of the mutual NDA occurs, the harmed party can take legal action. Remedies may include seeking monetary damages for any losses suffered or obtaining injunctive relief, which is a court order to stop the unauthorised disclosure of information.
Where can businesses find a free mutual NDA template?
Free mutual NDA templates are widely available online from legal resource sites and universities. However, these should be used with caution. It is always best to have legal counsel review any template to customise it for your specific business relationship and use contract management tools for tracking.
About the Company
Volody AI CLM is an Agentic AI-powered Contract Lifecycle Management platform designed to eliminate manual contracting tasks, automate complex workflows, and deliver actionable insights. As a one-stop shop for all contract activities, it covers drafting, collaboration, negotiation, approvals, e-signature, compliance tracking, and renewals. Built with enterprise-grade security and no-code configuration, it meets the needs of the most complex global organizations. Volody AI CLM also includes AI-driven contract review and risk analysis, helping teams detect issues early and optimize terms. Trusted by Fortune 500 companies, high-growth startups, and government entities, it transforms contracts into strategic, data-driven business assets.








