Krunal Shah
Feb 25, 2026

Key Highlights
Fixed-term contracts are a type of employment contract with a predetermined end date or project completion trigger.
They offer flexibility for employers but result in less job security for employees compared to permanent staff.
In India, these contracts are legal, but labour laws prevent their misuse to avoid offering permanent roles.
Employees on fixed-term agreements are entitled to fair treatment and many of the same rights as permanent workers.
The duration of employment is clearly defined, simplifying the termination process upon contract expiry.
Clear terms on renewal and termination are crucial for legal compliance.
Introduction
Are you considering different types of employment for your business or wondering about your rights as a temporary worker? Fixed-term employment is a common arrangement where an employee is hired for a specific employment period. These term contracts have a clear start and end date, making them useful for project-based work or seasonal needs. Understanding how they work is essential for both employers and employees to manage expectations and ensure all legal obligations are met. This guide explores the benefits and drawbacks of these agreements.
Defining Fixed Term Contracts

A fixed-term contract is a type of employment agreement established for a specific period. This means the employment relationship has a predetermined end date, which is either a set date or upon the completion of a particular project or task. These term contracts are designed for temporary employment needs.
Unlike a permanent contract, which continues indefinitely, this arrangement automatically concludes when the term expires. This fundamental difference in duration impacts aspects like job security and how the employment relationship ends, making it distinct from ongoing, permanent roles.
What is a Fixed Term Agreement in India?
In India, a fixed-term contract is a legally recognised employment agreement. Indian labour laws permit businesses to hire employees for a specific period of time, especially when the need is temporary or project-based. The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, provides the legal foundation for such arrangements, specifying that the non-renewal of an expired contract is not considered retrenchment.
However, the legal framework is designed to protect workers from exploitation. The courts have consistently ruled that employers cannot use successive fixed-term contracts to fill roles that are permanent in nature. This practice is seen as a way to bypass the statutory benefits and protections offered to permanent employees.
Therefore, while a fixed-term employment contract is legal, it must be used genuinely for temporary needs. Any attempt to use it as a substitute for permanent hiring can be challenged, ensuring that the rights of workmen are upheld under Indian labour laws.
Key Elements That Make a Contract ‘Fixed Term’
For an employment contract to be correctly classified as 'fixed-term', it must contain several crucial elements. These details provide clarity for both the employer and employee, defining the temporary nature of the fixed-term employment from the outset. A well-drafted agreement prevents future disputes and ensures legal compliance.
The most critical component is the clear specification of the duration of employment. This defines the exact length of the work relationship and sets clear expectations.
Key information that should always be included in a fixed-term employment contract includes:
Period of Employment: The contract must clearly state the start date and the predetermined end date or the specific project completion criteria.
Termination Clause: It should outline the terms for early termination, including any required notice period from either party.
Contract Renewal: The agreement should specify if and how the contract can be renewed, clarifying whether it happens automatically or requires a new contract.
Related Article: Contract End Date: When Does Your Contract End?
Fixed Term Contracts vs. Permanent Contracts
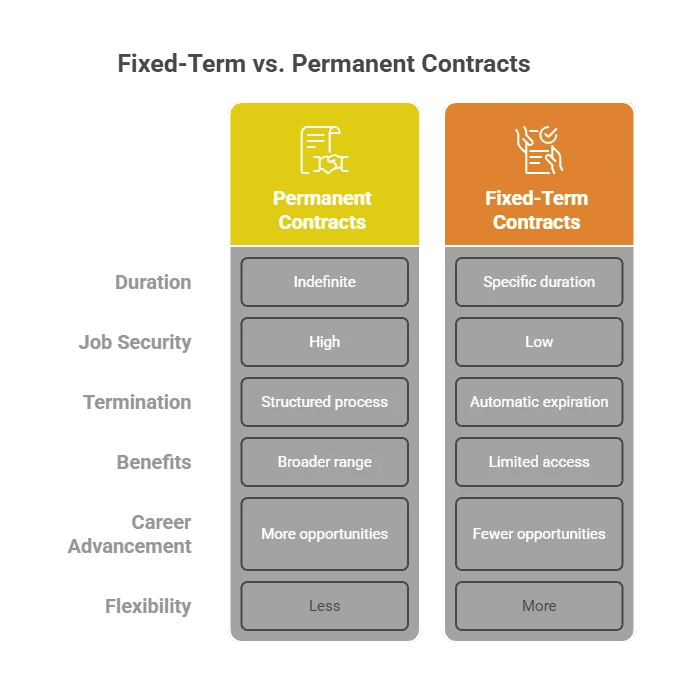
The primary distinction between fixed-term and permanent employment lies in the contract's duration. A permanent contract, also known as an indefinite contract, has no specified end date and continues until an employee resigns or their employment is terminated by the employer. This creates an ongoing employment relationship.
In contrast, a term employment contract is defined by its limited employment period. It has a clear beginning and an end. While employees in both arrangements often share similar rights, this difference in duration is fundamental. Let's look closer at the core differences between these two common types of employment contracts.
Core Differences Between Fixed Term and Permanent Employment
When comparing a fixed-term contract with a permanent one, the most significant differences revolve around job security and termination. A permanent employee enjoys a higher degree of job security, as their role is ongoing. The process of terminating a permanent staff member is also more regulated under employment laws to prevent unfair dismissal.
Conversely, an employee on a fixed-term contract has employment for a pre-defined period only. Their employment automatically ends upon the contract's expiry without any need for a formal termination process, which results in less long-term security.
Here is a simple breakdown of the core differences:
Feature | Fixed-Term Contract | Permanent Contract |
|---|---|---|
Duration | Has a specified end date or is tied to a project's completion. | Has no predetermined end date and continues indefinitely. |
Job Security | Lower, as employment is temporary by design. | Higher, as the role is ongoing and long-term. |
Termination | Ends automatically when the contract expires. | Continues until the employee resigns or is terminated by the employer, often with notice. |
How Fixed Term Contracts Compare With Casual Employment
While both fixed-term contracts and casual employment are forms of temporary work, they are structurally very different. A fixed-term contract offers a more formalised arrangement with a commitment for a specific period and usually involves regular hours. It provides a greater degree of predictability for both the employer and the employee.
Casual employment, on the other hand, is far more flexible and less secure. It is often used for freelancers or gig workers who are brought in on an as-needed basis. There is typically no guarantee of a minimum number of hours or ongoing work.
Key distinctions include:
Schedule: Fixed-term employees often have regular hours, whereas casual workers have no guaranteed number of hours.
Commitment: Fixed-term contracts bind both parties for a specific duration, while casual agreements offer more flexibility but less security.
Rights: Employees on fixed-term contracts generally have more employment rights and protections compared to casual workers, who may be considered self-employed.
Legal Status of Fixed Term Agreements in India

Fixed-term employment contracts have a clear and established legal status in India. They are legitimised under key labour laws, most notably the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947. This legislation acknowledges that certain jobs are temporary by nature and allows for contracts that expire after a set period.
However, this legal recognition comes with responsibilities. Employers must ensure legal compliance and cannot use these agreements to disguise permanent work. Indian labour laws include provisions to prevent the misuse of such contracts, protecting workers' rights. Understanding these rules is vital for any business utilising a fixed-term employment contract.
Labour Laws and Rules Governing Fixed Term Contracts
The legal framework for fixed-term employment in India is primarily shaped by the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947. Section 2(oo)(bb) of this Act specifically excludes the non-renewal of an expired contract from the definition of retrenchment. This provision legally permits fixed-term employment and means that standard severance dues are not payable upon the contract's natural expiry.
A critical rule under Section 25B is that employers must follow relates to 'continuous service'. If an employee works for more than 240 days in a 12-month period, they may gain protections similar to those of permanent workers, even on a fixed-term contract. Courts actively scrutinise cases where employers create artificial breaks in service to avoid this rule.
Given these complexities, seeking legal advice is wise. It ensures your employment laws are correctly applied, your early termination clause is fair, and your contracts do not unintentionally create permanent employment obligations. The judiciary often looks at the true nature of the work to determine if a contract is genuinely temporary.
Rights and Protections for Employees on Fixed Term Agreements
Employees on fixed-term agreements are entitled to fair treatment and should not be treated less favourably than their permanent counterparts. While their job security is inherently limited by the contract's duration, employment laws provide significant protections to ensure their rights are respected during the employment period.
These individuals are entitled to all statutory benefits applicable to salaried employees. This ensures a level playing field and prevents employers from using temporary contracts simply to cut costs on essential employee welfare.
Key rights and protections for fixed-term employees include:
Equal Pay and Benefits: They are entitled to the same pay and conditions as permanent employees doing similar work.
Statutory Leave: This includes entitlements like sick leave, paid holidays, and maternity leave, as per applicable laws.
Access to Facilities: They should have access to company facilities like canteens or childcare.
Information on Vacancies: Employers must inform them about permanent vacancies within the company.
When Should Businesses Use Fixed Term Contracts?

Deciding when to use a fixed-term employment contract is a key part of strategic workforce planning. These contracts are ideal when your business needs are temporary and well-defined. They allow you to bring in temporary workers with specific skills for a set duration without the commitment of a permanent hire.
This approach gives you the flexibility to scale your workforce up or down in response to fluctuating demands, project cycles, or employee absences. It is a practical tool for managing resources effectively. Below, we explore some common scenarios where these contracts are most beneficial.
Common Scenarios for Fixed Term Agreement Use
Businesses turn to fixed-term agreements in a variety of situations where employment is needed for a specified period. These contracts provide a clear and straightforward solution for temporary staffing gaps, ensuring that operations continue smoothly without the need for a permanent hiring commitment.
This type of contract is particularly useful when the work itself has a natural end point. For example, a project with a clear deadline or a seasonal peak in demand are perfect fits for this employment model. The possibility of contract renewal can also be built in if project needs evolve.
Common scenarios for using fixed-term agreements include:
Seasonal Work: Hiring additional staff during peak business periods, such as the holiday season in retail or harvest time in agriculture.
Specific Project Needs: Employing specialists to work on a particular project with a defined start and end date.
Maternity Cover: Covering the role of a permanent employee who is away on maternity leave.
Temporary Initiatives: Staffing pilot programs or other short-term business initiatives.
Advantages for Employers When Using Fixed Term Contracts
For employers, fixed-term contracts offer significant advantages, primarily centred around flexibility and cost-effectiveness. They are a powerful tool for agile workforce planning, allowing a business to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and internal business needs without long-term financial obligations.
This model is especially beneficial when you need specialised skills for a specific project. It allows you to access expertise for a set duration of employment without committing to a permanent role that may not be needed once the project is complete.
Key advantages for employers are:
Flexibility: Easily adjust staffing levels to meet short-term demands or project-based work.
Cost-Effectiveness: Avoid the long-term costs associated with permanent hires, especially for temporary tasks.
Access to Specialised Skills: Bring in experts for a specific project without a permanent commitment.
Simplified Termination: The employment relationship ends automatically at the contract's conclusion, simplifying the offboarding process.
Related Article: Types of Contracts Every Business Needs
Main Benefits of Fixed Term Contracts

The primary benefits of fixed-term employment are rooted in flexibility and opportunity. For employers, this flexibility allows them to manage their workforce efficiently, responding to project demands without over-committing resources. It is an effective way to handle temporary staffing needs.
For employees, these contracts can be a gateway to gaining valuable experience or working in a way that fits their lifestyle. Project-based employment offers a chance to develop new skills and build a diverse portfolio, potentially leading to a permanent role or a new contract. Let's explore these benefits in more detail.
Flexibility for Employers and Workers
Flexibility is arguably the greatest benefit of a fixed-term contract. For employers, it means having the agility to respond to fluctuating business needs. You can hire staff for a busy season, cover for an absent employee, or bring in an expert for a specific task, all without the long-term commitment of a permanent hire. The specific terms of the contract, including the notice period, give you control over your staffing levels.
For workers, this flexibility can also be appealing. Fixed-term or temporary work provides an opportunity to gain experience in different industries, develop a range of skills, and build a professional network. It can serve as a stepping stone to a permanent position or suit individuals who prefer project-based work over a long-term role.
This arrangement allows both parties to enter an employment relationship with a clear, shared understanding of its temporary nature. It provides a structured way to meet immediate needs while leaving future options open.
Opportunities for Project-Based Employment
Fixed-term contracts are perfectly suited for project-based employment. When your company undertakes a specific project with a defined timeline, hiring permanent staff may not be practical. A fixed-term agreement allows you to bring in the exact talent you need for the duration of that project, ensuring you have the right skills at the right time.
This type of employment relationship is built around achieving the goals of a specific project. The employment period is directly tied to the project’s lifecycle. Once the work is complete, the contract naturally concludes, providing a clean end to the engagement.
Furthermore, if the project needs to be extended or a new phase begins, there is often an option for contract renewal. This gives you the ability to retain valuable team members who are already familiar with the work, ensuring continuity and efficiency. It is a strategic way to manage talent for time-bound initiatives.
Related Article: 5 Employment Contract Pitfalls You Can Easily Avoid
Key Drawbacks and Challenges of Fixed Term Agreements

Despite their benefits, fixed-term agreements come with significant drawbacks, especially for employees. The primary challenge is job insecurity, as the employment is for a limited time. This temporary nature means employees have less job security compared to their permanent colleagues, which can affect morale and commitment.
For employers, challenges can arise with early termination if it’s not handled correctly. A poorly written termination clause can lead to legal disputes. We will now look at these issues, including concerns over job security and the complexities of ending a contract.
Job Security Concerns and Limited Benefits
The most significant disadvantage of a fixed-term contract for an employee is the lack of long-term job security. Knowing your job has a firm end date can be stressful and makes financial planning difficult. This constant uncertainty can negatively impact morale and an employee’s sense of belonging within the company.
In some cases, temporary workers may also have limited access to certain company benefits. While they are legally entitled to statutory benefits, they might miss out on perks offered to permanent staff, such as comprehensive health insurance plans or participation in long-term incentive schemes. This can create a two-tier system where employees doing similar work receive different levels of compensation and support.
Because their employment is for a limited time, these workers may feel less integrated into the company culture. This can make it difficult for employers to build cohesive teams and foster a strong sense of loyalty.
Ending or Renewing a Fixed Term Contract: What Employers & Employees Need to Know
Understanding the process for ending or renewal of a fixed-term contract is crucial for both employers and employees to avoid misunderstandings and legal issues. The standard procedure is for the contract to end automatically on its specified end date, with no further action needed from either party.
However, situations involving early termination or contract renewal require careful handling. If either party wishes to end the contract before its expiry, they must follow the early termination clause outlined in the agreement. This typically involves providing a formal notice of termination.
Here are the key points to remember:
Natural Expiry: The contract ends on the specified end date unless renewed.
Contract Renewal: Renewal is not automatic unless stated. It usually requires signing a new contract or an extension agreement.
Early Termination: This must comply with the contract's termination clause, including any required notice period, to avoid claims of unfair dismissal.
Successive Contracts: Be aware that in some jurisdictions, including India, using multiple successive contracts can lead to the employee being deemed permanent.
Related Article: Renewing Contracts :Effective Strategies for Success
Conclusion
In summary, understanding fixed term contracts is essential for both employers and employees navigating the modern workplace. These agreements offer flexibility and can be advantageous for project-based roles, but they also come with challenges, such as concerns over job security and limited benefits. It's crucial to weigh these pros and cons carefully, ensuring that both parties are aware of their rights and responsibilities. By doing so, businesses can make more informed decisions regarding their workforce, while employees can better understand their position within these agreements. If you have further questions or need assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out for a consultation to explore your options in detail.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Fixed Term Contract Be Renewed or Extended in India?
Yes, a fixed-term contract can be renewed or extended in India by signing a new contract. However, Indian labour laws scrutinise successive renewals for the same role. If the period of employment becomes excessively long, courts may interpret it as a way to avoid granting permanent status and its associated benefits.
What Must Be Included in a Fixed Term Agreement?
A fixed-term employment contract must clearly state its predetermined end date or completion criteria. It should also include the job role, compensation, and specific terms regarding renewal. A well-defined early termination clause, detailing the process for a notice of termination, is also essential for legal clarity.
What Happens If a Fixed Term Contract Ends Early?
If a fixed-term contract ends early, the terms of the termination clause must be followed. This usually requires one party to give the other a specified notice period. Failure to adhere to this clause can lead to legal claims, such as for unfair dismissal, so ensuring legal compliance is critical.
About the Company

Volody AI CLM is an Agentic AI-powered Contract Lifecycle Management platform designed to eliminate manual contracting tasks, automate complex workflows, and deliver actionable insights. As a one-stop shop for all contract activities, it covers drafting, collaboration, negotiation, approvals, e-signature, compliance tracking, and renewals. Built with enterprise-grade security and no-code configuration, it meets the needs of the most complex global organizations. Volody AI CLM also includes AI-driven contract review and risk analysis, helping teams detect issues early and optimize terms. Trusted by Fortune 500 companies, high-growth startups, and government entities, it transforms contracts into strategic, data-driven business assets.